Nylon 6 6 is a widely utilized synthetic fiber that has become a staple in numerous industries, thanks to its remarkable characteristics. This article explores the intricate chemical structure of Nylon 6 6, its distinct features, and how it compares with other types of nylon.
Chemical Structure of Nylon 6 6
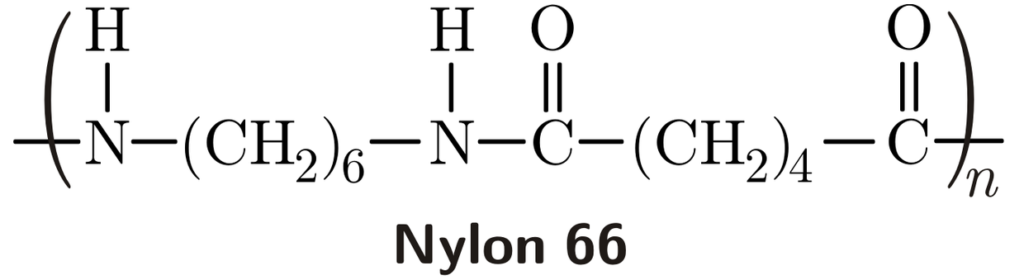
Nylon 6 6 stands out due to its specific chemical composition, which comprises repeating units of six carbon atoms, six hydrogen atoms, and six nitrogen atoms. This structure originates from a condensation polymerization process where adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine react. The high crystallinity of the resulting polymer lends it superior strength and durability.
Exceptional Strength and Toughness
One of the defining qualities of Nylon 6 6 is its impressive strength and toughness. The polymer chains exhibit a regular and repeating pattern, facilitating robust intermolecular bonding. This results in a material highly resistant to abrasion, tearing, and impacts, making it ideal for demanding applications.
Superior Chemical Resistance
Nylon 6 6’s resistance to a wide array of chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents, sets it apart from other types of nylon. This resistance is particularly advantageous in environments where exposure to harsh chemicals is frequent, such as in the automotive and aerospace sectors.
High Thermal Stability
The ability of Nylon 6 6 to endure high temperatures without degradation is another significant advantage. This thermal stability is crucial for applications involving elevated temperatures, like electrical insulation and various automotive parts, where material integrity must be maintained.
Comparing Nylon 6 6 with Other Nylons
Compared to other nylons, such as Nylon 6 and Nylon 12, Nylon 6 6 exhibits superior properties. Nylon 6 has a lower melting point and reduced chemical resistance, while Nylon 12, with its lower crystallinity, is less strong and durable. These differences make Nylon 6 6 the preferred choice for more demanding applications.
Applications in the Textile Industry
In textiles, Nylon 6 6 is prized for creating high-quality fabrics used in clothing, including suits, dresses, and sportswear. Its blend of strength, durability, and resistance to wear makes it ideal for fabric production, ensuring longevity and performance.
Applications in the Automotive Industry
Nylon 6 6 is extensively used in the automotive industry to manufacture engine components, transmission parts, and interior trims. Its resilience to chemicals and thermal stability makes it suitable for the rigorous conditions found in automotive applications.
Applications in the Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry leverages Nylon 6 6 for aircraft and spacecraft components such as landing gear, fuel lines, and electrical insulation. Its high strength-to-weight ratio and chemical resistance are critical in the demanding aerospace environment.
Conclusion
Nylon 6 6 is a versatile and highly functional synthetic fiber celebrated across various industries for its unique properties. Its combination of strength, toughness, chemical resistance, and thermal stability makes it an indispensable material in many modern applications. As advancements continue, Nylon 6 6 is poised to remain integral in the development of new, innovative products.
Nylon 6 6 FAQ
Nylon 6 6 is a versatile synthetic polymer used in numerous applications across various industries due to its exceptional properties. Below, we address some frequently asked questions to provide a comprehensive understanding of Nylon 6 6.
1. What is Nylon 6 6?
Nylon 6 6 is a type of synthetic polymer known as a polyamide. It is produced through the polymerization of hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid. The “6 6” in its name refers to the six carbon atoms present in each of these monomers, which gives Nylon 6 6 its distinctive structure and properties.
2. How is Nylon 6 6 Different from Other Types of Nylon?
Nylon 6 6 differs from other types of nylon, such as Nylon 6 and Nylon 12, primarily in its chemical structure and resulting properties:
- Nylon 6: Has a lower melting point and is more susceptible to chemical degradation compared to Nylon 6 6. It is produced from a single monomer (caprolactam).
- Nylon 12: Features a lower degree of crystallinity, making it less strong and tough than Nylon 6 6. It is made from dodecanolactam.
These differences affect their suitability for various applications, with Nylon 6 6 often chosen for more demanding environments.
3. What Are the Key Properties of Nylon 6 6?
Nylon 6 6 is celebrated for several unique properties:
- High Strength and Toughness: Its regular polymer chain structure provides robust intermolecular forces, leading to superior strength and durability.
- Chemical Resistance: Excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents.
- Thermal Stability: Can withstand high temperatures without degrading, making it suitable for applications involving heat.
- Abrasion Resistance: Highly resistant to wear and tear, extending the lifespan of products made from it.
4. In Which Industries is Nylon 6 6 Commonly Used?
Nylon 6 6 is used across various industries due to its versatile properties:
- Textile Industry: For high-quality fabrics in clothing like suits, dresses, and sportswear.
- Automotive Industry: In engine components, transmission parts, and interior trims.
- Aerospace Industry: For aircraft and spacecraft components, such as landing gear and fuel lines.
- Consumer Goods: In products like kitchen utensils, gears, and mechanical parts due to its durability.
5. What are the Benefits of Using Nylon 6 6 in Textiles?
In the textile industry, Nylon 6 6 is favored for its combination of strength, durability, and resistance to abrasion. Fabrics made from Nylon 6 6 maintain their shape, resist wear, and are long-lasting, making them ideal for everyday clothing and performance wear.
6. How Does Nylon 6 6 Perform in High-Temperature Environments?
Nylon 6 6 has excellent thermal stability, meaning it can endure high temperatures without significant degradation. This makes it suitable for applications such as electrical insulation and automotive parts, where it must maintain integrity and performance even under thermal stress.
7. What Makes Nylon 6 6 Resistant to Chemicals?
The chemical resistance of Nylon 6 6 is due to its tightly packed, crystalline structure. This makes it less permeable to many substances, providing excellent resistance to a broad range of chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents. This property is crucial for applications in harsh chemical environments.
8. Are There Any Drawbacks to Using Nylon 6 6?
While Nylon 6 6 has many advantages, there are some considerations:
- Cost: Nylon 6 6 can be more expensive compared to other types of nylon or synthetic materials.
- Moisture Absorption: It can absorb moisture from the environment, which might affect its dimensional stability and mechanical properties over time.
Despite these, its benefits often outweigh the drawbacks in many high-performance applications.
9. How is Nylon 6 6 Manufactured?
Nylon 6 6 is produced through a condensation polymerization process. This involves reacting adipic acid with hexamethylenediamine under heat, causing the formation of water as a by-product and creating long polymer chains. These chains are then cooled and spun into fibers or molded into shapes for various applications.
10. Why Choose Nylon 6 6 Over Other Materials?
Nylon 6 6 is often chosen for applications that require a combination of high strength, toughness, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. Its ability to perform well in harsh conditions makes it ideal for demanding environments in various industries, providing a durable and reliable material solution.