Introduction
Nylon is one of the most versatile and widely used synthetic polymers, and among its various types, Nylon 11 and Nylon 12 stand out for their unique properties. Nylon 11 vs nylon 12, both materials belong to the family of aliphatic polyamides and offer distinct benefits depending on their intended use. Understanding the differences between Nylon 11 and Nylon 12 is crucial for choosing the right material for specific applications. In this article, we will delve into the chemical properties, advantages, disadvantages, and real-world applications of both materials, providing you with a comprehensive guide to help you make an informed decision.
Properties of Nylon 11
Nylon 11, also known as polyamide 11, is a bio-based polymer derived primarily from castor oil. It is known for its high impact strength, flexibility, and excellent chemical resistance, which makes it suitable for a range of demanding applications. Here’s a breakdown of its key properties:
Chemical Structure and Properties
Nylon 11 has a long-chain molecular structure with 11 carbon atoms in its repeating unit. This structure contributes to its improved flexibility, toughness, and resistance to moisture absorption. It’s less prone to hydrolysis compared to other nylons, which makes it suitable for wet environments.Applications in Various Industries
Nylon 11 is often used in the automotive, aerospace, and electrical industries, where parts are exposed to harsh conditions. It’s used for fuel lines, hydraulic hoses, electrical connectors, and coatings due to its superior chemical and thermal stability.Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:- High chemical resistance, especially to oils and fuels.
- Excellent low-temperature performance and flexibility.
- Bio-based and more environmentally friendly due to its castor oil origins.
Disadvantages:
- Relatively expensive compared to other nylons.
- May be more difficult to process in certain applications.
Properties of Nylon 12
Nylon 12, or polyamide 12, is another aliphatic polyamide known for its superior performance in various applications. Unlike Nylon 11, which is bio-based, Nylon 12 is typically derived from petroleum-based raw materials. Let’s explore its characteristics:
Chemical Structure and Properties
Nylon 12 has a shorter molecular chain than Nylon 11, with 12 carbon atoms in its repeating unit. This results in greater flexibility and lower moisture absorption. Nylon 12 also exhibits improved dimensional stability and better resistance to wear and tear.Applications in Various Industries
Like Nylon 11, Nylon 12 is used in automotive, industrial, and medical sectors. It is commonly found in products like tubing, fuel lines, and flexible films, as well as medical devices such as catheters and drug delivery systems.Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:- Lower moisture absorption than many other nylons, leading to better dimensional stability.
- Better wear resistance and smoother surface finish.
- More cost-effective compared to Nylon 11.
Disadvantages:
- Less resistant to oils and fuels compared to Nylon 11.
- Less bio-based, making it less environmentally friendly than Nylon 11.
Comparison of Nylon 11 and Nylon 12
When choosing between Nylon 11 and Nylon 12, several factors come into play. Let’s compare the two materials across various parameters to better understand their performance.
Mechanical Properties
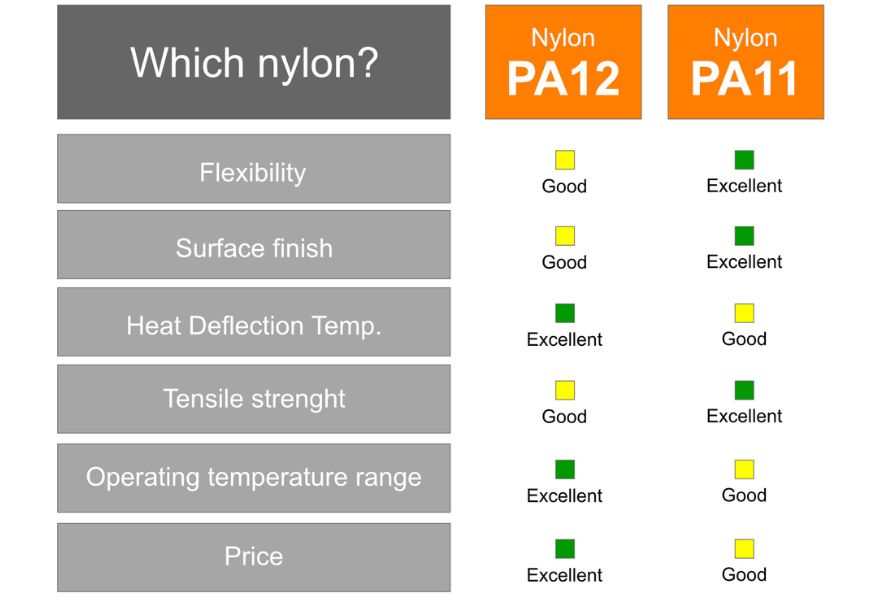
Nylon 11 has superior impact resistance and is generally more flexible, making it ideal for applications where toughness and flexibility are crucial. However, Nylon 12 offers better wear resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring smooth surfaces and low friction.Chemical Resistance
Nylon 11 excels in chemical resistance, particularly in environments exposed to oils, fuels, and harsh chemicals. Nylon 12, while still durable, does not perform as well in these conditions.Thermal Properties
Both Nylon 11 and Nylon 12 have good thermal stability, but Nylon 11 has a higher melting point, making it more suitable for high-temperature applications. Nylon 12, on the other hand, offers better low-temperature flexibility.Cost Comparison
Nylon 12 is generally more affordable than Nylon 11 due to its petroleum-based production. Nylon 11’s bio-based nature, while environmentally beneficial, contributes to its higher cost.
Nylon 11 vs Nylon 12, Which is Better?
The decision to use Nylon 11 or Nylon 12 depends on several factors, including the specific requirements of your application. Here are some key considerations:
Factors to Consider
- Environmental Conditions: For high-temperature and fuel-resistant applications, Nylon 11 may be the better choice. However, if low moisture absorption and dimensional stability are more important, Nylon 12 might be preferable.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Nylon 12 is generally less expensive and might be the go-to option for applications with lower mechanical demands.
- Environmental Impact: Nylon 11 is more eco-friendly due to its bio-based origin, while Nylon 12’s petroleum-based production makes it less sustainable.
Case Studies of Successful Applications with Each Material
- Nylon 11 in Automotive: Fuel lines and hydraulic hoses in the automotive industry benefit from Nylon 11’s resistance to oils and extreme temperatures, ensuring long-lasting performance.
- Nylon 12 in Medical: In the medical field, Nylon 12 is widely used for medical tubing, catheters, and drug delivery systems due to its low moisture absorption and biocompatibility.
Conclusion of Nylon 11 vs Nylon 12
In conclusion, both Nylon 11 and Nylon 12 offer distinct advantages depending on the application. Nylon 11 stands out for its chemical resistance, impact strength, and bio-based composition, making it ideal for harsh, high-performance environments. On the other hand, Nylon 12 offers superior flexibility, wear resistance, and lower cost, making it a suitable option for applications requiring smooth finishes and dimensional stability.
When choosing between these two materials, consider factors such as cost, environmental impact, and the specific performance requirements of your project. By weighing these considerations, you can make an informed decision that meets your functional and budgetary needs.
FAQ of Nylon 11 vs Nylon 12
What are the main differences between Nylon 11 and Nylon 12?
Nylon 11 is bio-based and more resistant to oils and fuels, while Nylon 12 has better wear resistance and lower moisture absorption.Which material is more suitable for high-performance applications?
Nylon 11 is generally better for high-performance applications that require chemical resistance and flexibility, particularly in automotive and aerospace industries.Is one material more environmentally friendly than the other?
Yes, Nylon 11 is more environmentally friendly because it is derived from castor oil, while Nylon 12 is produced from petroleum-based raw materials.
By understanding these differences, you can confidently choose the right nylon material for your specific needs.
