Въвеждане на найлон 6 и 66
Найлон 6: Кристална трайност и цветово разнообразие
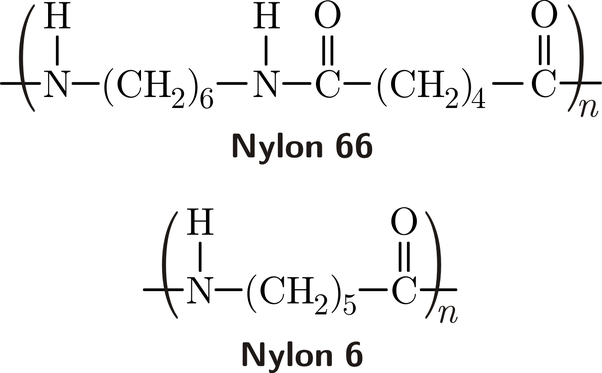
Найлон 6, наричан още полиамид 6, има кристална структура, изградена от шест въглеродни и шест водородни атома. Тази присъща структура му осигурява забележителни механични качества като якост на опън и устойчивост на удар. Неговата изключителна устойчивост на износване допълнително повишава пригодността му за приложения, изискващи дълготрайност. Отличната боядисваемост на найлон 6 разширява употребата му в различни естетически сфери.
Найлон 66: Гъвкава здравина и химическа устойчивост
Найлон 66, или полиамид 66, има същия въглероден и водороден състав като найлон 6. Въпреки това подреждането му дава по-гъвкава и по-малко кристална структура. Това различие придава на найлон 66 по-висока якост на опън, устойчивост на удар и химическа устойчивост. Изключителната му устойчивост на топлина го прави незаменим за среди, изискващи температурна издръжливост.
Универсални приложения: Полза за различни индустрии
В областта на текстила найлонът 6 намира широко приложение в текстила, килимите и въжетата, като се използват неговите механични качества и устойчивост на износване. Освен това, той допринася за автомобилни компоненти като ремъци, зъбни колела и лагери, благодарение на стабилното си съотношение между здравина и тегло.
Адаптивността на найлон 66 се проявява в спортното облекло и бельото благодарение на неговата устойчивост на износване и боядисване. Благодарение на своята химическа и топлинна устойчивост той играе ключова роля и в промишлеността, като се използва в зъбни колела, лагери и електроизолационни материали. Освен това той е предпочитан материал при производството на гуми, като се отличава с устойчивост на износване и якост на опън.
Заключение: Предефиниране на гъвкавостта
В обобщение, найлон 6 и найлон 66 предлагат различни свойства, пригодени за различни приложения. Найлон 6 се отличава със своята устойчивост на износване и възможности за боядисване, което го прави основен продукт в текстилния и автомобилния сектор. В същото време химическата и топлинната устойчивост на найлон 66 го превръща в жизненоважен актив в промишлеността и автомобилостроенето. И двата материала са пример за гъвкавост, като се интегрират безпроблемно в множество индустрии.
Често задавани въпроси за найлон 6 и 66
1.Какво представляват найлон 6 и 66?
Найлон 6 и найлон 66 са два вида синтетични полимери, известни също като полиамиди, с различен химичен състав и свойства. Те се използват широко в различни индустрии поради уникалните си характеристики.
2. Какви са разликите между найлон 6 и 66?
Основната разлика е в молекулярната им структура. Найлон 6 се състои от повтарящи се единици от шест въглеродни и шест водородни атома, докато найлон 66 има подобен състав, но с различно разположение на тези единици. Това структурно различие води до разлики в свойствата, като гъвкавост, кристалност и устойчивост на топлина.
3. Какви свойства притежава найлон 6?
Найлон 6 се характеризира с висока кристалност, отлични механични свойства (включително якост на опън и устойчивост на удар), изключителна устойчивост на износване и добра боядисваемост. Тези свойства го правят подходящ за приложения, изискващи дълготрайност, здравина и многофункционалност на цветовете.
4. Какви свойства притежава найлон 66?
Найлон 66 притежава по-висока устойчивост на топлина, химическа устойчивост и гъвкавост в сравнение с найлон 6. Освен това той има висока якост на опън, удължение и отлична устойчивост на химикали и разтворители. Тези свойства го правят подходящ за приложения, които изискват устойчивост в тежки условия.
5. Какви са най-често срещаните приложения на найлон 6?
Найлон 6 намира широко приложение в производството на текстил, килими, въжета, автомобилни компоненти (като ремъци, зъбни колела и лагери) и различни естетически приложения. Отличната му устойчивост на износване и боядисване го правят предпочитан избор в тези индустрии.
6. Какви са най-често срещаните приложения на найлон 66?
Найлон 66 обикновено се използва в производството на облекло (особено спортно облекло и бельо), промишлени части (като зъбни колела и лагери), електроизолационни материали и гуми. Изключителната му топлоустойчивост, химическа устойчивост и механична якост го правят незаменим в тези приложения.
7. Могат ли найлоните 6 и 66 да се рециклират?
Да, и найлон 6, и найлон 66 могат да се рециклират. Процесите на рециклиране на тези материали включват разтопяване на найлоновите отпадъци за повторна употреба в различни приложения, което допринася за усилията за устойчивост и намаляване на въздействието върху околната среда.
8. Има ли някакви ограничения или съображения при използването на Nylon 6 и 66?
Макар че найлоните 6 и 66 предлагат многобройни предимства, от съществено значение е да се вземат предвид фактори като абсорбция на влага, устойчивост на UV лъчи и специфична химическа съвместимост в зависимост от предвиденото приложение. Освен това трябва да се спазват подходящи техники за обработка и боравене, за да се оптимизират характеристиките и дълготрайността.