NYLON 66 FEATURE
✔ Low Moisture Absorption
✔ High Tensile Strength
✔ Good Abrasion Resistance
✔ Good electrical insulation

Nylon 66, also known as PA66, is a popular engineering plastic prized for its exceptional strength, stiffness, heat resistance, and wear resistance. These properties make it a go-to material for a wide range of applications across various industries.
Variations of Nylon 66 for Specific Needs:
PA66 GF13: This variation incorporates 13% glass fiber reinforcement, enhancing mechanical strength and stiffness compared to standard PA66.
VOSS PA66 GF35 and Bosch PA66 GF30: These are brand-specific variations likely formulated by Voss and Bosch, respectively. They contain 35% and 30% glass fiber reinforcement, potentially targeting applications requiring increased strength.
Choosing the Right Nylon 66 Variation:
The optimal choice between these Nylon 66 variations depends on your project’s specific requirements. Consider factors like:
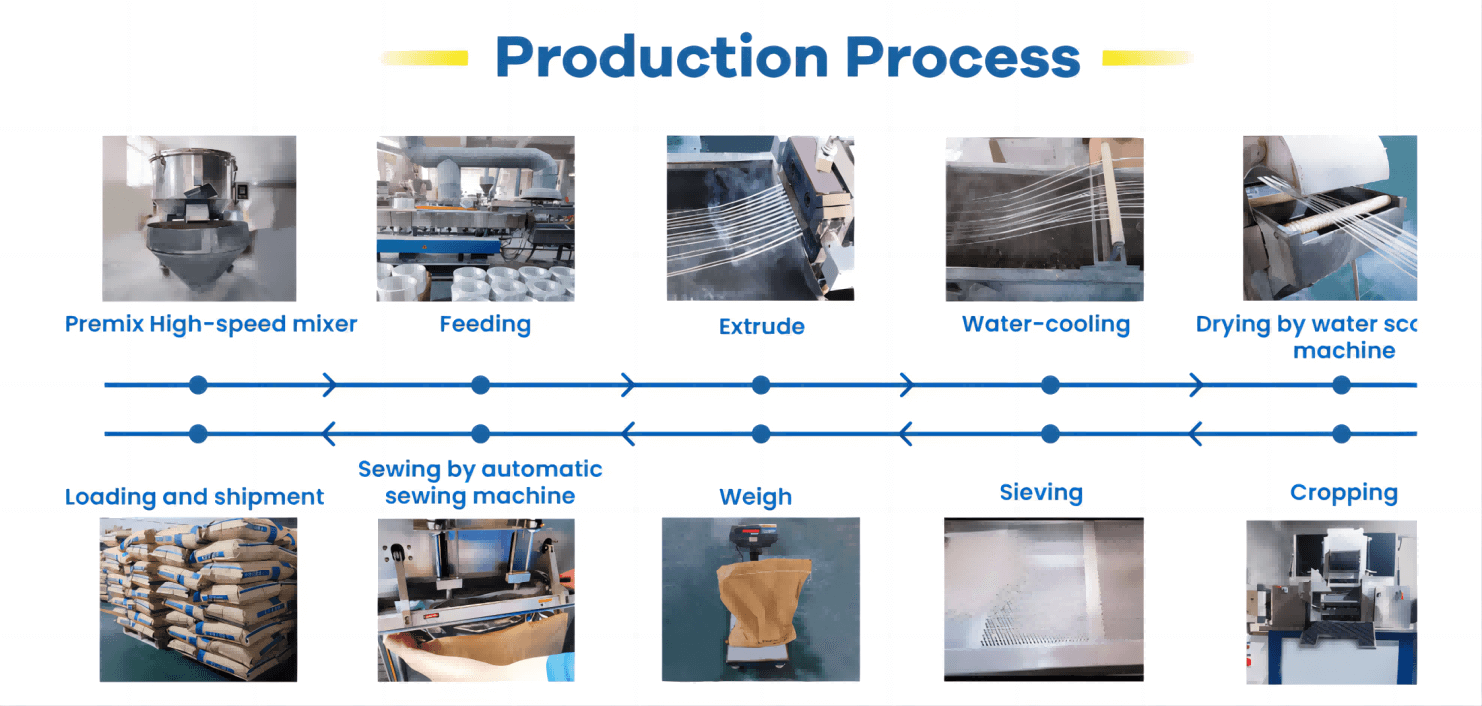
PA66 resin is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent mechanical properties.
Strong, heat-resistant plastic reinforced with tiny glass fibers for increased stiffness and durability.
High-strength PA66 enhanced with reinforcing materials for superior stiffness, durability, and heat resistance.
Fire-resistant PA66 plastic with added flame retardants for enhanced safety in demanding applications.
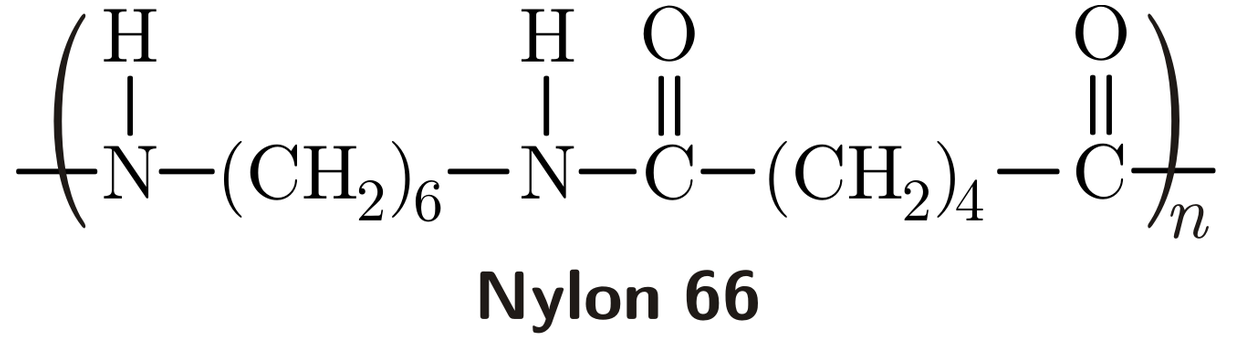
Nylon 66 is a type of nylon, a synthetic polymer known for its strength, elasticity, and versatility. It’s formed by reacting two different chemicals, hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid.
While similar, Nylon 6 and Nylon 66 have some key differences:
PA66 has a wide range of applications due to its properties. Here are some examples: