Dans le domaine des matériaux composites, le PA66 GF50 se distingue par sa polyvalence et ses performances élevées. Composé de nylon 66 (polyamide 66) renforcé par de la fibre de verre 50% (GF), le PA66 GF50 offre un mélange exceptionnel de résistance, de rigidité et de stabilité thermique. Le choix du matériau composite idéal pour un projet spécifique est crucial, car les différentes options possèdent des propriétés variées qui peuvent avoir un impact significatif sur la fonctionnalité et les performances.
Comprendre le PA66 GF50
1.1 Qu'est-ce que le PA66 GF50 ?
Le PA66 GF50 est un matériau composite formé par la combinaison d'une résine de nylon 66 et de fibres de verre 50% hachées ou continues. Le nylon 66, également connu sous le nom de polyamide 66, est un thermoplastique technique robuste réputé pour ses excellentes propriétés mécaniques et sa stabilité dimensionnelle. Les fibres de verre, quant à elles, confèrent au composite une résistance et une rigidité exceptionnelles.
1.2 Le rôle de la fibre de verre dans le PA66 GF50
L'incorporation de fibres de verre 50% dans la matrice de nylon 66 améliore considérablement les performances mécaniques du PA66 GF50. Les fibres de verre agissent comme un agent de renforcement, répartissant efficacement les contraintes dans le matériau et renforçant sa résistance à la traction, son module de flexion et sa résistance aux chocs. Cela se traduit par un composite capable de supporter des charges importantes, ce qui le rend adapté à des applications exigeantes.
1.3 Applications haute fréquence du PA66 GF50
Ses propriétés impressionnantes en font un candidat de choix pour les applications nécessitant une grande résistance et une stabilité dimensionnelle à des fréquences élevées. Ces caractéristiques sont particulièrement utiles dans les secteurs suivants :
- Électricité et électronique : Il est utilisé dans divers composants électriques en raison de ses bonnes propriétés d'isolation électrique et de sa capacité à conserver sa forme sous des charges électriques à haute fréquence. Les applications comprennent les composants structurels des transformateurs, les isolateurs et les bobines.
- Industrie automobile :L'industrie automobile utilise le PA66 GF50 pour les pièces qui nécessitent un équilibre entre résistance, rigidité et légèreté. Il s'agit par exemple de composants de moteurs, de carters d'engrenages et de composants sous le capot.
Comparaison entre le PA66 GF50 et d'autres composites
2.1 Matériaux composites courants
Il existe une vaste gamme de matériaux composites, chacun possédant des propriétés uniques qui répondent à des applications spécifiques. Voici une comparaison avec certains des matériaux de substitution les plus courants :
- Plastique renforcé de fibres de carbone (PRFC) :Le PRFC offre le rapport résistance/poids le plus élevé parmi ces options, mais son coût est nettement plus élevé. Il est idéal pour les applications nécessitant une résistance exceptionnelle et légère, comme les composants aérospatiaux.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiène Styrène) :L'ABS est un thermoplastique rentable et polyvalent, connu pour sa bonne résistance aux chocs et sa facilité de mise en œuvre. Cependant, l'ABS n'est pas à la hauteur du PA66 GF50 en termes de résistance mécanique et de stabilité thermique.
- Polycarbonate (PC) :Le PC offre une excellente résistance aux chocs, une grande clarté et une grande stabilité dimensionnelle. Tout en possédant de bonnes propriétés mécaniques, il n'égale pas le PA66 GF50′ en termes de performances soutenues à haute température.
- Polyéthylène haute densité (PEHD) :Le PEHD est une option économique et légère qui présente une bonne résistance aux produits chimiques. Cependant, sa résistance mécanique et sa rigidité sont inférieures à celles du PEHD.
2.2 Propriétés mécaniques
En ce qui concerne les propriétés mécaniques, il excelle en termes de résistance à la traction, de module de flexion et de résistance aux chocs. L'incorporation de fibres de verre améliore considérablement ces propriétés par rapport aux nylons non renforcés ou à d'autres thermoplastiques tels que l'ABS ou le PC.
2.3 Propriétés thermiques
Il présente une bonne stabilité thermique, offrant une température de déflexion à la chaleur plus élevée que beaucoup d'autres thermoplastiques. Cela lui permet d'être performant dans les applications exposées à une chaleur modérée. Toutefois, pour les environnements à très haute température, le CFRP ou d'autres composites à haute performance peuvent être plus appropriés.
2.4 Propriétés électriques
Le PA66 GF50 présente de bonnes propriétés d'isolation électrique, ce qui en fait un matériau précieux pour les composants électriques. Bien qu'il ne soit pas le composite le plus isolant disponible, il offre un bon équilibre entre les propriétés électriques et la résistance mécanique.
2.5 Coût et disponibilité
Il s'agit d'un matériau composite rentable par rapport à des options plus performantes comme le CFRP.
Avantages du PA66 GF50
3.1 Résistance mécanique supérieure
Le PA66 GF50 présente une résistance mécanique exceptionnelle, ce qui en fait un choix idéal pour les applications exigeant des capacités de charge élevées. Le renforcement apporté par les fibres de verre améliore considérablement sa résistance à la traction, son module de flexion et sa résistance aux chocs, ce qui lui permet de supporter des forces et des impacts importants.
3.2 Stabilité thermique
Le PA66 GF50 présente une bonne stabilité thermique, conservant sa forme et ses propriétés sur une large gamme de températures. Cette caractéristique le rend adapté aux applications impliquant une exposition modérée à la chaleur. Bien qu'il ne soit pas le composite le plus résistant à la chaleur disponible, il offre un équilibre entre la stabilité thermique et la rentabilité.
3.3 Isolation électrique
Le PA66 GF50 possède de bonnes propriétés d'isolation électrique, ce qui en fait un matériau précieux pour les composants électriques. Sa capacité à résister au flux de courant électrique permet d'éviter les courts-circuits et de garantir la sécurité de fonctionnement des systèmes électriques. Bien qu'il ne soit pas le composite le plus isolant disponible, il offre un équilibre pratique entre les propriétés électriques et la résistance mécanique.
3.4 Rapport coût-efficacité
Le PA66 GF50 est un matériau composite relativement économique par rapport à des options plus performantes comme le CFRP. Il s'agit donc d'un choix intéressant pour les applications où les contraintes budgétaires sont un facteur. L'équilibre entre ses propriétés et son prix en fait un matériau polyvalent pour une large gamme d'applications.
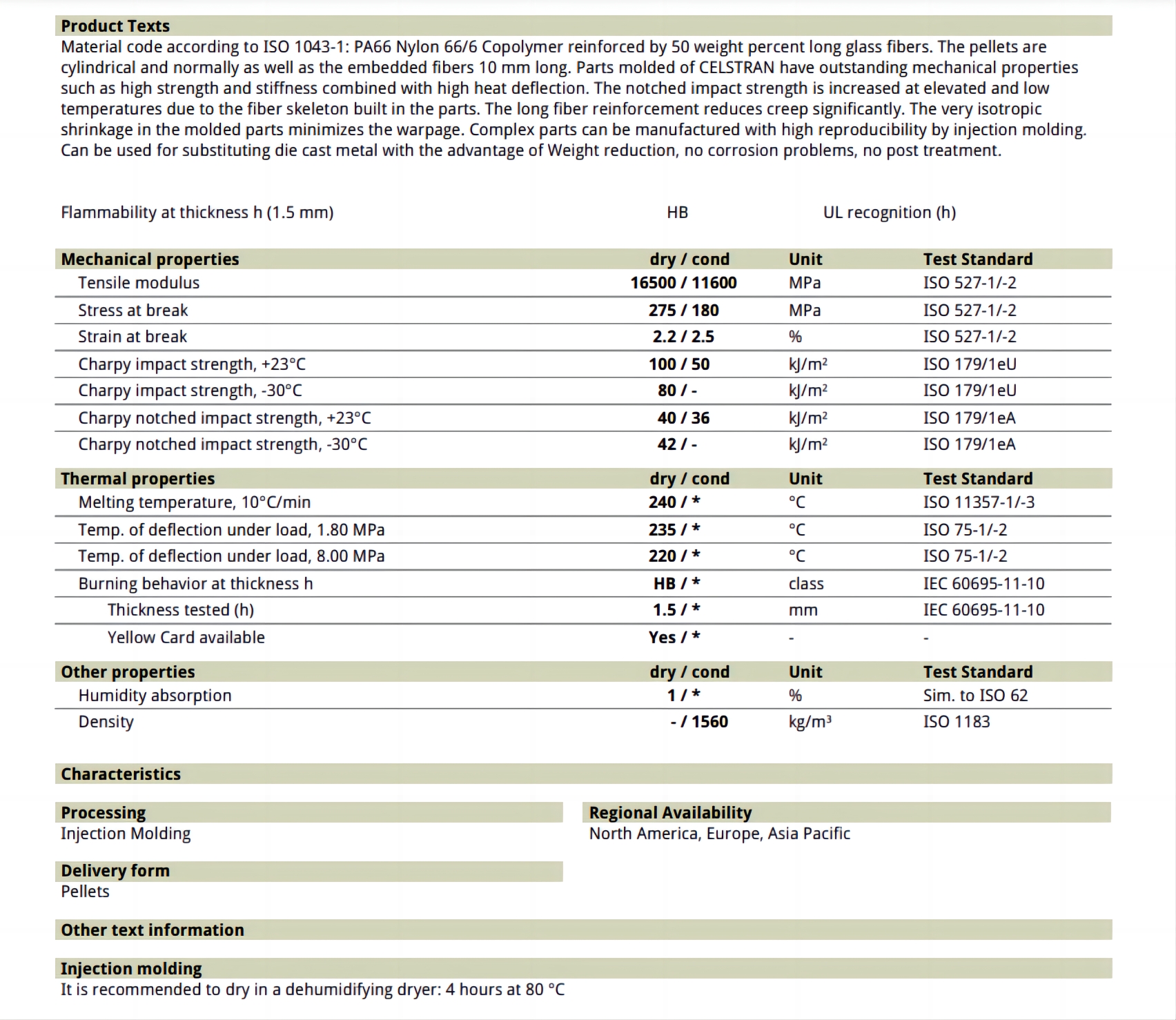
Fiche technique PA66 GF50
Limites du PA66 GF50
4.1 Considérations relatives au poids
S'il est plus léger que les métaux, il est plus lourd que d'autres thermoplastiques tels que l'ABS ou le PEHD. Ce facteur de poids doit être pris en compte lorsque l'optimisation du poids est une exigence essentielle de la conception. Dans ce cas, le CFRP ou d'autres composites légers peuvent être plus appropriés.
4.2 Défis liés à la transformation et à la fabrication
Son traitement et sa fabrication peuvent être plus complexes que ceux des thermoplastiques non renforcés. La présence de fibres de verre peut poser des problèmes lors du moulage, de l'usinage et d'autres processus de fabrication. Un outillage et une expertise spécialisés peuvent être nécessaires pour garantir des pièces de haute qualité.
4.3 Préoccupations environnementales et sanitaires
Les fibres de verre posent des problèmes de santé potentiels en cas d'inhalation ou d'ingestion. Des précautions de sécurité appropriées et des équipements de protection individuelle doivent être utilisés lors de la manipulation et du traitement de ces fibres afin de minimiser l'exposition. En outre, l'élimination des déchets générés pendant la fabrication doit respecter les réglementations environnementales.
Applications du PA66 GF50
5.1 Industrie automobile
L'industrie automobile l'utilise largement pour divers composants en raison de ses propriétés de résistance, de rigidité et de légèreté. Les applications sont les suivantes :
- Composants du moteur : Collecteurs d'admission, couvercles de soupapes et conduits d'admission d'air
- Carters d'engrenages : Transmissions, différentiels et boîtes de transfert
- Composants sous le capot : Supports de batterie, carénages de ventilateur et supports de radiateur
5.2 Électricité et électronique
Il est largement utilisé dans les composants électriques et électroniques en raison de ses propriétés d'isolation électrique et de sa capacité à conserver sa forme sous des charges électriques à haute fréquence. En voici quelques exemples :
- Composants structurels des transformateurs : Entretoises isolantes, douilles et supports de bobinage
- Isolateurs : Douilles haute tension, entretoises et espaceurs
- Bobines : Pour l'enroulement de bobines électriques dans les moteurs, les transformateurs et les solénoïdes.
5.3 Équipements industriels
Les équipements industriels en dépendent pour leur solidité, leur rigidité et leur résistance à l'usure. Les applications les plus courantes sont les suivantes
- Pièces de machines : Engrenages, roulements et paliers
- Composants du convoyeur : Rouleaux, pignons et guides de chaîne
- Protections : Boucliers de sécurité, couvercles de machines et enceintes
5.4 Biens de consommation
Il se retrouve dans divers produits de consommation en raison de sa durabilité et de son attrait esthétique. En voici quelques exemples :
- Articles de sport : Clubs de golf, skis et snowboards
- Outils à main : Boîtiers de perceuse, manches de tournevis et manches de clé à molette
- Petits appareils : Cafetières, mixeurs et robots ménagers
Faire le bon choix pour votre projet
6.1 Évaluer les exigences du projet
Le choix du matériau composite approprié pour un projet commence par une évaluation approfondie des exigences et des contraintes spécifiques. Il faut tenir compte de facteurs tels que
- Charges mécaniques :Les forces et les contraintes auxquelles le matériau devra résister
- Température de fonctionnement :La gamme de températures à laquelle le matériau sera exposé
- Exigences électriques :Nécessité d'une isolation électrique
- Considérations relatives au poids :Si l'optimisation du poids est un facteur critique
- Capacités de traitement :Les méthodes de fabrication et de production disponibles
- Contraintes de coût :Le budget alloué au matériel
6.2 Analyse coûts-avantages
Une fois les exigences du projet définies, il convient de procéder à une analyse coûts-avantages afin de comparer les différentes options en matière de composites. Il faut prendre en compte le coût initial du matériau, les coûts de transformation et le potentiel à long terme.
Foire aux questions (FAQ)
1. Quelle est la principale différence entre le PA66 GF50 et les autres composites à base de fibres de verre ?
La principale différence entre le PA66 GF50 et les autres composites à base de fibres de verre réside dans le type de matrice de résine utilisée. Le PA66 GF50 utilise la résine de nylon 66, alors que les autres composites peuvent utiliser des résines différentes comme l'époxy ou le polyester. Le choix de la résine influence les propriétés globales du composite, notamment sa résistance mécanique, sa stabilité thermique et sa résistance chimique.
2. Le PA66 GF50 est-il plus cher que les autres composites ?
Son coût varie en fonction de facteurs tels que la qualité spécifique, le fournisseur et la quantité. Toutefois, en général, il est considéré comme un matériau composite relativement rentable par rapport aux options à haute performance comme le PRFC. Il offre un équilibre entre les propriétés et le prix, ce qui le rend adapté à une large gamme d'applications.
3. Le PA66 GF50 peut-il être utilisé dans des environnements à haute température ?
Il présente une bonne stabilité thermique, ce qui le rend adapté aux applications impliquant une exposition modérée à la chaleur. Il peut supporter des températures de fonctionnement continues jusqu'à environ 180°C (356°F) et une exposition de courte durée à des températures plus élevées. Cependant, pour les environnements à très haute température, d'autres composites à haute performance comme le CFRP ou les polyimides peuvent s'avérer plus appropriés.
4. Comment les propriétés d'isolation électrique du PA66 GF50 se comparent-elles à celles d'autres composites ?
Le PA66 GF50 possède de bonnes propriétés d'isolation électrique, ce qui en fait un matériau précieux pour les composants électriques. Bien qu'il ne soit pas le composite le plus isolant disponible, il offre un équilibre pratique entre les propriétés électriques et la résistance mécanique. Pour les applications nécessitant le plus haut niveau d'isolation électrique, des matériaux tels que le PTFE ou le PEEK sont plus appropriés.
Le PA66 GF50 est un matériau composite polyvalent et économique qui offre une combinaison convaincante de résistance mécanique, de stabilité thermique et de propriétés d'isolation électrique. Sa capacité à supporter des charges importantes, à conserver sa forme sous une chaleur modérée et à résister au courant électrique en fait un choix précieux pour une large gamme d'applications. Lors de la sélection du composite approprié pour un projet, il convient d'examiner attentivement les exigences spécifiques, les contraintes de coût et les capacités de traitement afin de s'assurer que le matériau choisi correspond aux objectifs du projet. Le PA66 GF50, qui a fait ses preuves et qui est polyvalent, est un matériau qui mérite d'être pris en considération pour un large éventail d'applications.

