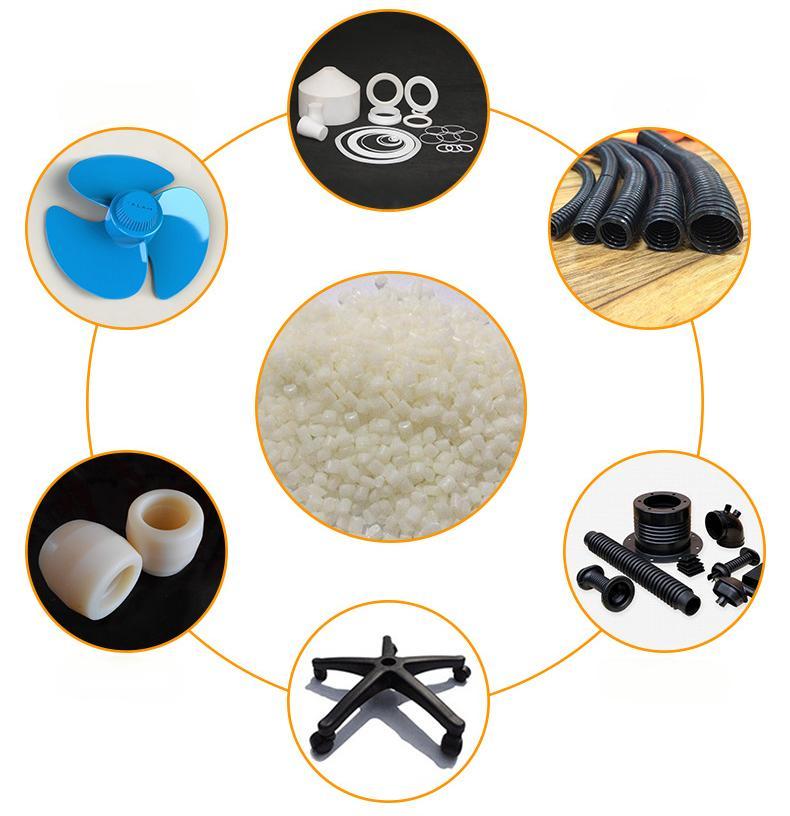
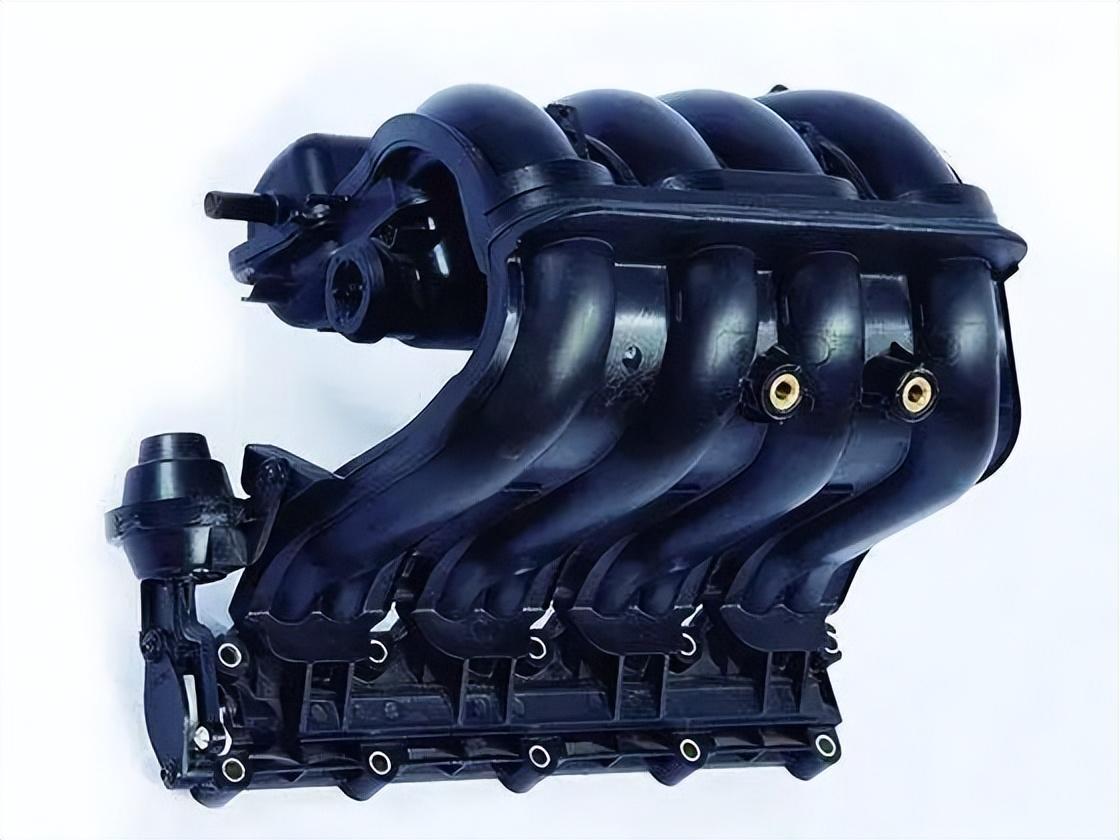
Vysoko výkonný nylon 6
Nylon 6 (PA6) je pracovný plast známy svojou pevnosťou, pružnosťou a odolnosťou proti opotrebovaniu. Ponúkame rôzne možnosti PA6, ktoré spĺňajú vaše špecifické potreby:
- Nevystužený PA6: Základný materiál, ktorý ponúka vyvážené vlastnosti pre každodenné použitie.
- PA6+GF (vystužený sklenenými vláknami): Zvýšte pevnosť a tuhosť pomocou rôznych možností obsahu vlákien, ako sú PA6 GF30 (30% sklenené vlákno) a PA6 GF50 (50% sklenené vlákno). Ideálne pre nosné diely s vysokým zaťažením.
- PA6 GB (vystužený sklenenými guličkami): PA6 GB20 GF10 napríklad ponúka lepšiu rozmerovú stabilitu a odolnosť proti opotrebovaniu v porovnaní s nevystuženým PA6. Obsah sklenených guličiek 10% zachováva dobrý pomer pevnosti a hmotnosti.
Náš rozmanitý výber plastov PA6 vám zaručí, že nájdete ideálnu voľbu pre svoj projekt. Či už potrebujete všestrannosť nevystuženého PA6 alebo zvýšenú pevnosť možností vystužených sklenenými vláknami alebo guličkami, máme pre vás riešenie. Kontaktujte nás ešte dnes, aby ste prediskutovali svoj projekt a preskúmali naše riešenia z nylonu 6!
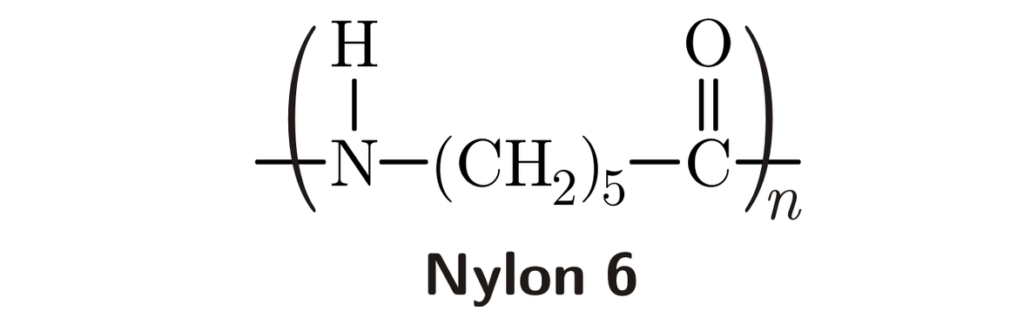
Typy nylonu 6
PA6 sklenené vlákno
Silný plast so sklenenými vláknami na zvýšenie výkonu dielov.
PA6 spomaľovač horenia
Ohňovzdorný PA6: Zvýšená bezpečnosť pre nylon 6 s dobrými vlastnosťami.
PA6 Odolnosť proti chladu
PA6: Zostáva odolný aj v mrazivých teplotách. Výkon pri nízkych teplotách.
Často kladené otázky o nylone 6
Čo je to nylon 6?
Nylon 6 je typ termoplastického polyméru, ktorý je známy svojou pevnosťou, pružnosťou a odolnosťou proti oderu. Vďaka svojej univerzálnosti sa široko používa v rôznych aplikáciách.
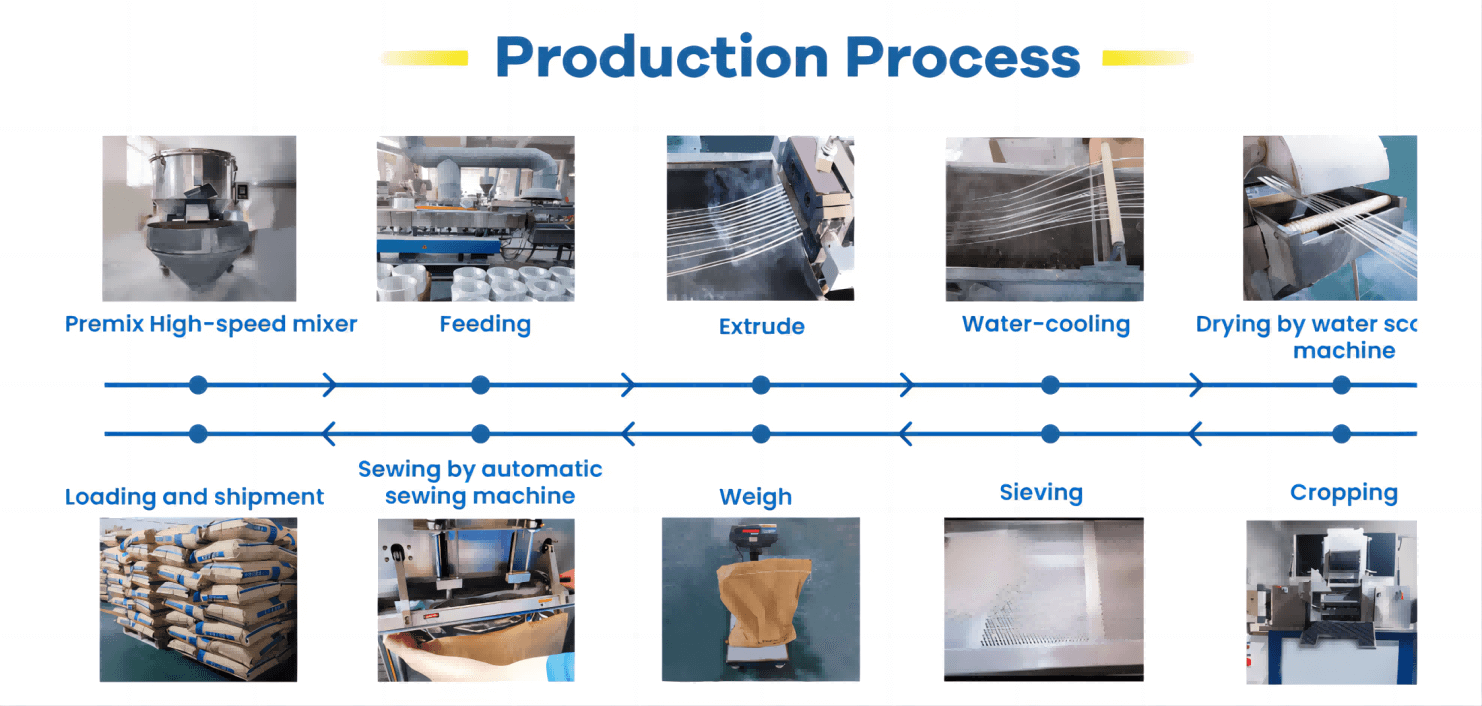
Ako sa vyrába nylon 6?
Nylon 6 sa zvyčajne vyrába procesom nazývaným liata polymerizácia. Tu je zjednodušené rozdelenie:
- Príprava monoméru: Získava sa kaprolaktám, stavebný prvok nylonu 6.
- Topenie: Kaprolaktám sa roztaví a premení na roztavený prstenec.
- Polymerizácia: Kruhové molekuly reagujú a spájajú sa do dlhých polymérnych reťazcov nylonu 6.
- Tvarovanie: Roztavený nylon 6 sa naleje do foriem a nechá sa stuhnúť do požadovaného tvaru.
Tento proces umožňuje dobrú rozmerovú stabilitu konečného výrobku v porovnaní s niektorými inými metódami.
Ako sa nylon 6 líši od nylonu 66?
Oba sú nylóny, ale s malými rozdielmi v ich chemickej štruktúre. Z toho vyplývajú niektoré kľúčové rozdiely:
- Absorpcia vody: Nylon 6 absorbuje viac vlhkosti, čo ovplyvňuje rozmerovú stabilitu a teplotu ohybu.
- Tepelná odolnosť: Nylon 66 má vyššiu teplotu tepelnej deformácie v dôsledku nižšej absorpcie vody.
- Chemická odolnosť: Nylon 66 má o niečo lepšiu odolnosť voči niektorým chemikáliám.
Aké sú aplikácie nylonu 6?
Vďaka svojim vlastnostiam má nylon 6 množstvo aplikácií vrátane:
- Vlákna: Na textílie, ako sú koberce, oblečenie a športové oblečenie.
- Technické diely: Ozubené kolesá, ložiská a iné komponenty vyžadujúce odolnosť proti opotrebovaniu.
- Automobilové diely: Komponenty ako kryty ventilátorov a časti motora.
- Elektrické aplikácie: Izolácia pre vodiče a káble.
Aký je rozdiel medzi PA6+GF30, PA6 GB20 GF10 a PA6 GF50?
Všetky tieto zápisy sa vzťahujú na varianty plastu PA6 plneného sklenenými vláknami. Kľúčový rozdiel spočíva v percentuálnom obsahu sklenených vlákien:
- PA6+GF30: Tento materiál obsahuje 30% sklenených vlákien v hmotnosti. Ponúka dobrú rovnováhu medzi pevnosťou, tuhosťou a hmotnosťou.
- PA6 GB20 GF10: Toto označenie je trochu iné. PA6 GB20 pravdepodobne označuje špecifickú triedu PA6 s ďalšími vlastnosťami (GB20 by mohol byť kód výrobcu). Obsahuje aj sklenené vlákna 10%. Tento materiál by mohol ponúkať mierne odlišné vlastnosti v porovnaní so štandardným PA6+GF10 v dôsledku špecifickej triedy PA6.
- PA6 GF50: Tento materiál má spomedzi uvedených možností najvyšší obsah sklenených vlákien (50%). Je najpevnejší a najtuhší, ale aj najťažší a potenciálne krehkejší.