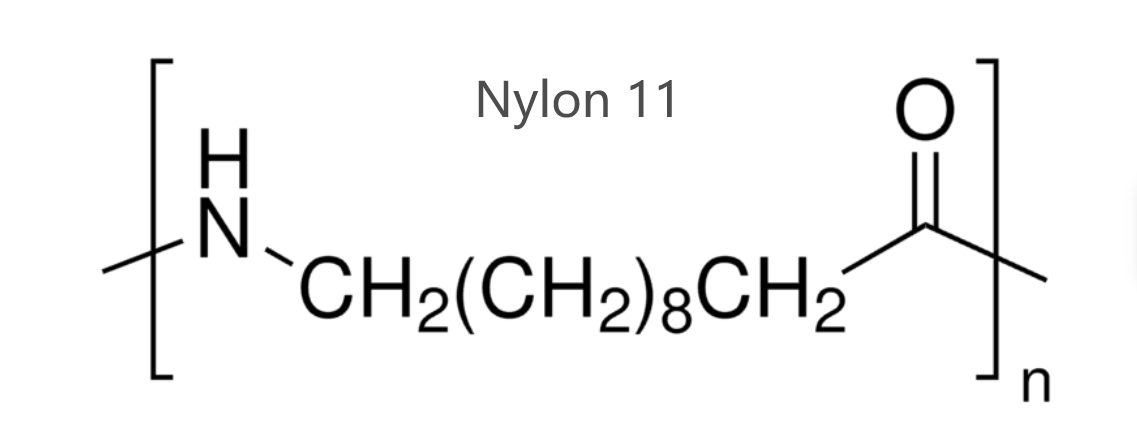
NYLON 11 FEATURE
✔ High Strength
✔ Excellent Flexibility
✔ Good UV Resistance
✔ Good Chemical Resistance
✔ Low Moisture Absorption

Nylon 11, also known as polyamide 11 (PA 11), is a high-performance plastic known for its exceptional balance of properties. Derived from castor beans, it’s a bioplastic option for those seeking sustainable materials.
Here’s what makes Nylon 11 stand out:
These properties make PA11 a versatile material used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, electrical, and consumer goods.
PA11 GF25 is a type of nylon plastic reinforced with 25% glass fibers for added strength.
PA11 GF30 is a nylon 11 plastic with 30% glass fiber reinforcement, making it stronger.
PA11 extrusion is a process to create shapes by forcing molten PA11 plastic through a mold.
PA11 extrusion compound is a pre-mixed PA11 plastic ready for extrusion processes.
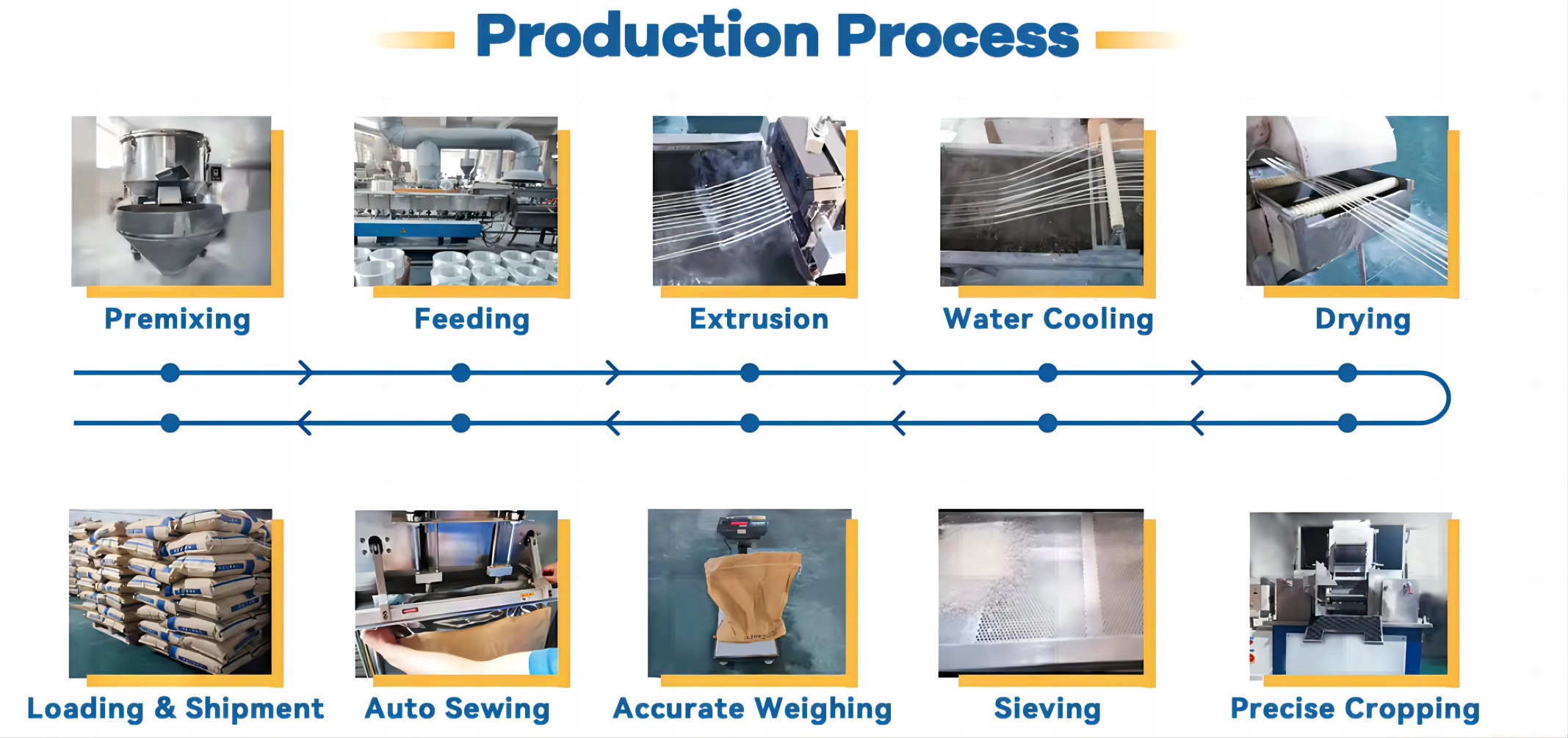
Nylon 11, which is also known as PA11, is a type of nylon resin known for its good impact resistance and flexibility.