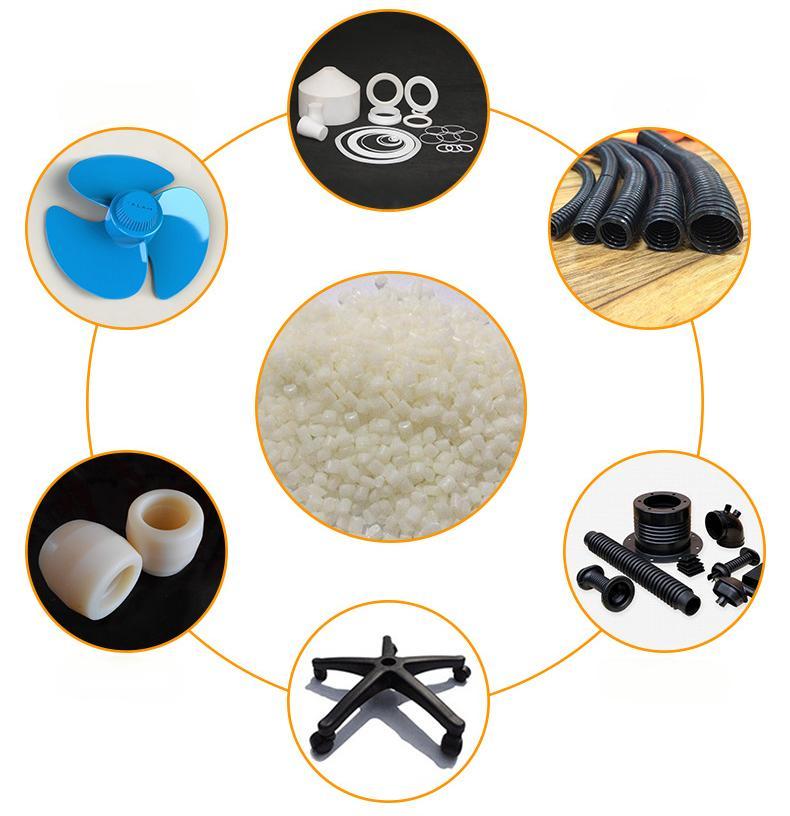
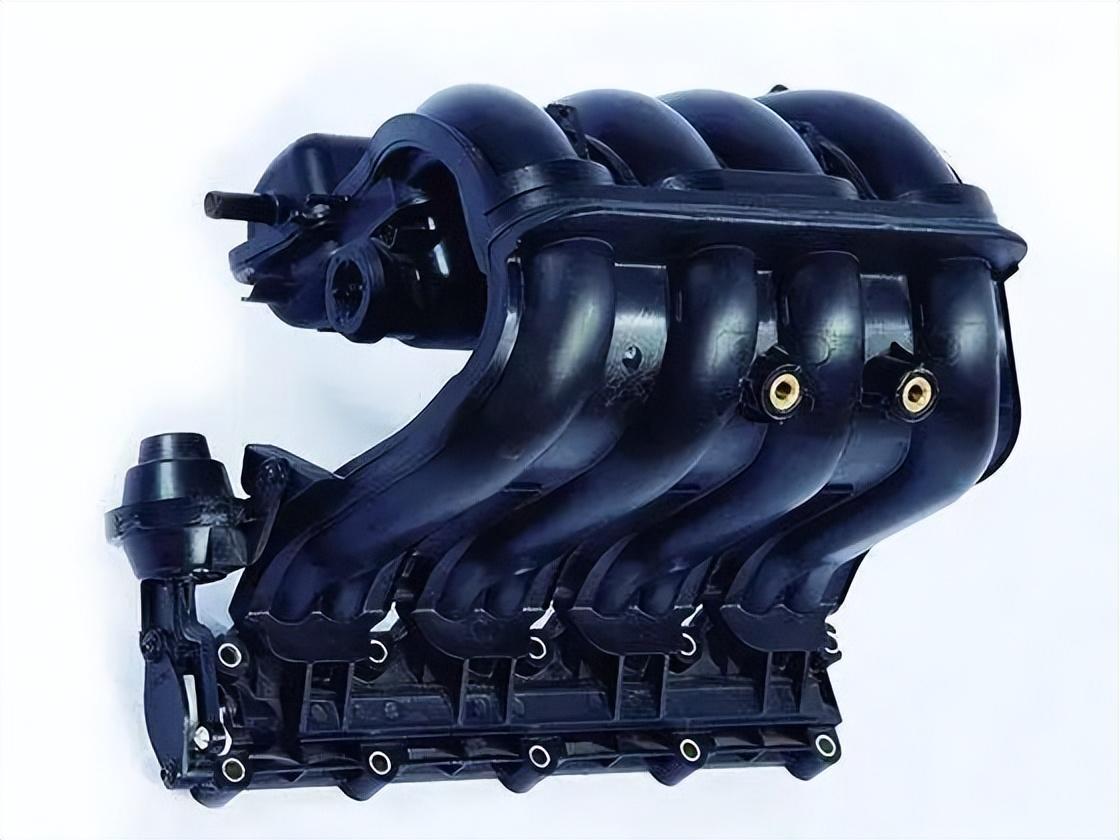
Nylon 6 o wysokiej wydajności
Nylon 6 (PA6) to tworzywo sztuczne znane ze swojej wytrzymałości, elastyczności i odporności na zużycie. Oferujemy różne opcje PA6, aby spełnić określone potrzeby:
- Niewzmocniony PA6: Materiał bazowy, oferujący równowagę właściwości do codziennych zastosowań.
- PA6+GF (wzmocniony włóknem szklanym): Zwiększ wytrzymałość i sztywność dzięki różnym opcjom zawartości włókien, takim jak PA6 GF30 (włókno szklane 30%) i PA6 GF50 (włókno szklane 50%). Idealny do części łożysk o dużym obciążeniu.
- PA6 GB (wzmocniony koralikami szklanymi): Na przykład PA6 GB20 GF10 oferuje lepszą stabilność wymiarową i odporność na zużycie w porównaniu do niewzmocnionego PA6. Zawartość koralików szklanych 10% zapewnia dobry stosunek wytrzymałości do masy.
Nasz zróżnicowany wybór tworzyw sztucznych PA6 zapewnia idealne dopasowanie do danego projektu. Niezależnie od tego, czy potrzebujesz wszechstronności niewzmocnionego PA6, czy zwiększonej wytrzymałości opcji wzmocnionych włóknem szklanym lub koralikami, mamy dla Ciebie wszystko. Skontaktuj się z nami już dziś, aby omówić swój projekt i poznać nasze rozwiązania Nylon 6!
Rodzaje Nylonu 6
Włókno szklane PA6
Mocne tworzywo sztuczne z włóknami szklanymi dla zwiększenia wydajności części.
Wzmocniony PA6
Wzmocniony PA6: Zwiększona wytrzymałość i odporność termiczna nylonu 6
PA6 Trudnopalny
Ognioodporny PA6: Zwiększone bezpieczeństwo nylonu 6 o dobrych właściwościach.
PA6 Odporność na zimno
PA6: zachowuje wytrzymałość nawet w niskich temperaturach. Wydajność w niskich temperaturach.
Najczęściej zadawane pytania dotyczące Nylonu 6
Co to jest Nylon 6?
Nylon 6 to rodzaj termoplastycznego polimeru, znanego ze swojej wytrzymałości, elastyczności i odporności na ścieranie. Jest szeroko stosowany w różnych aplikacjach ze względu na swoją wszechstronność.
Jak powstaje Nylon 6?
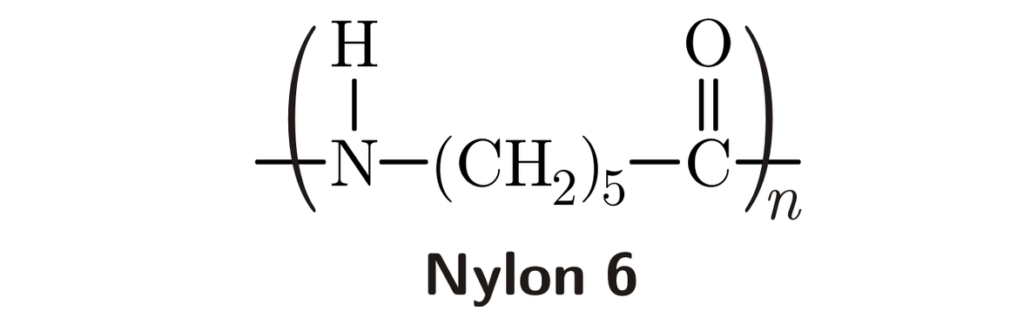
Nylon 6 jest zwykle wytwarzany w procesie zwanym polimeryzacją odlewniczą. Oto uproszczony podział:
- Przygotowanie monomeru: Otrzymuje się kaprolaktam, budulec Nylonu 6.
- Topienie: Kaprolaktam jest topiony i przekształcany w stopiony pierścień.
- Polimeryzacja: Cząsteczki w kształcie pierścienia reagują i łączą się, tworząc długie łańcuchy polimerowe Nylonu 6.
- Kształtowanie: Stopiony Nylon 6 jest wlewany do form i pozostawiony do zestalenia do pożądanego kształtu.
Proces ten zapewnia dobrą stabilność wymiarową produktu końcowego w porównaniu z niektórymi innymi metodami.
Czym różni się Nylon 6 od Nylonu 66?
Oba są nylonami, ale mają niewielkie różnice w strukturze chemicznej. Prowadzi to do kilku kluczowych różnic:
- Absorpcja wody: Nylon 6 pochłania więcej wilgoci, wpływając na stabilność wymiarową i temperaturę ugięcia.
- Odporność na ciepło: Nylon 66 ma wyższą temperaturę ugięcia ze względu na niższą absorpcję wody.
- Odporność chemiczna: Nylon 66 oferuje nieco lepszą odporność na niektóre chemikalia.
Jakie są zastosowania Nylonu 6?
Ze względu na swoje właściwości, Nylon 6 ma wiele zastosowań, w tym:
- Włókna: Do tekstyliów, takich jak dywany, odzież i odzież sportowa.
- Części techniczne: Koła zębate, łożyska i inne elementy wymagające odporności na zużycie.
- Części samochodowe: Komponenty takie jak osłony wentylatorów i części silnika.
- Zastosowania elektryczne: Izolacja przewodów i kabli.
Jaka jest różnica między PA6+GF30, PA6 GB20 GF10 i PA6 GF50?
Wszystkie te notacje odnoszą się do odmian tworzywa PA6 wypełnionych włóknami szklanymi. Kluczowa różnica polega na procentowej zawartości włókna szklanego:
- PA6+GF30: Materiał ten zawiera wagowo 30% włókien szklanych. Oferuje dobrą równowagę między wytrzymałością, sztywnością i wagą.
- PA6 GB20 GF10: To oznaczenie jest nieco inne. PA6 GB20 prawdopodobnie odnosi się do konkretnego gatunku PA6 o dodatkowych właściwościach (GB20 może być kodem producenta). Zawiera on również włókna szklane 10%. Materiał ten może oferować nieco inne właściwości w porównaniu do standardowego PA6+GF10 ze względu na specyficzny gatunek PA6.
- PA6 GF50: Materiał ten charakteryzuje się najwyższą zawartością włókna szklanego (50%) spośród wymienionych opcji. Będzie on najmocniejszy i najsztywniejszy, ale także najcięższy i potencjalnie bardziej kruchy.